Importance of email authentication protocols for security
In today’s fast-paced digital environment, understanding the importance of email authentication protocols is essential for ensuring secure and trustworthy communication. With increasing reliance on email for business transactions and personal correspondence, ensuring that emails are sent from verified sources has become paramount. This comprehensive guide will delve into the details of email authentication protocols, their significance in cybersecurity, their influence on brand reputation, practical implementation steps, and future trends aimed at enhancing email security.
Understanding Email Authentication Protocols
As the landscape of cyber threats evolves, so does the necessity for robust security measures to protect individuals and businesses alike. Email authentication protocols play a crucial role in verifying the legitimacy of email messages, safeguarding against malicious attacks, and maintaining user trust in digital communications.
Email authentication encompasses a variety of processes and technologies designed to ensure that emails are genuinely from the sender they claim to be from. By leveraging various protocols, organizations can confirm the identity of the sender, preventing spoofing and phishing attempts while also optimizing their email deliverability rates.
Definition and Purpose of Email Authentication
The primary goal of email authentication is to validate the source of an email message. At its core, email authentication aims to prevent fraudulent activities such as phishing, spam, and other forms of cybercrime that exploit email communications.
Implementing robust email authentication protocols protects not only businesses but also their customers and partners by creating a safer online environment. As a result, these protocols help build trust amongst users, which is vital in maintaining lasting relationships and ensuring a positive perception of the organization.
Key Types of Email Authentication Protocols
Several email authentication protocols are widely adopted within organizations to enhance their email security. The three principal protocols include:
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
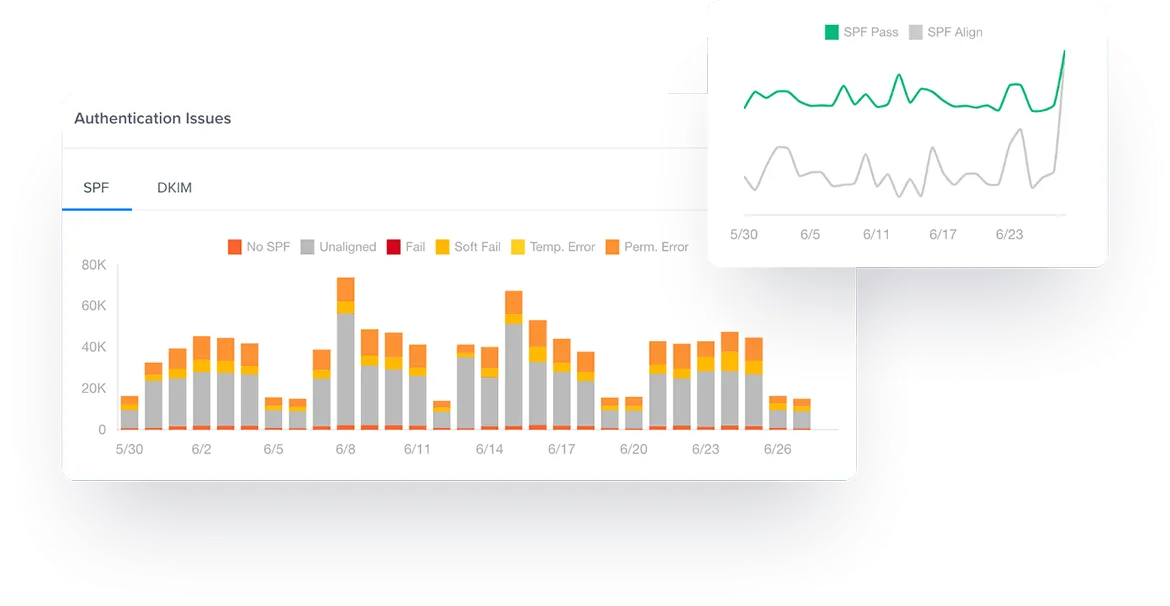
SPF is an essential mechanism that allows domain owners to specify which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of their domains. When a receiving mail server gets an email, it checks the sender’s IP address against the SPF record published in the DNS (Domain Name System). If the IP address matches an authorized server, the email passes authentication; if not, it may be flagged as suspicious or rejected altogether.
This protocol acts as a first line of defense against email spoofing, providing an efficient means for organizations to manage their email traffic. By implementing SPF, organizations can bolster their email integrity and reduce the risk of being impersonated by malicious actors.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
DKIM enhances email authentication by enabling the sender to attach a digital signature to the email header. This signature is created using the sender’s private key, allowing receiving mail servers to verify the authenticity of the message by checking the corresponding public key stored in the DNS records.
By validating the integrity of the email content, DKIM ensures that the message has not been altered during transmission. It also adds an extra layer of protection against phishing and spoofing attacks, further solidifying an organization’s email security posture.
To ensure that emails are not tampered with in transit, DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) uses encryption to verify the sender’s identity. Email marketing platforms like GetResponse and ActiveCampaign support DKIM configuration, allowing businesses to sign their emails digitally, increasing email authenticity and reducing the chances of being flagged as spam.
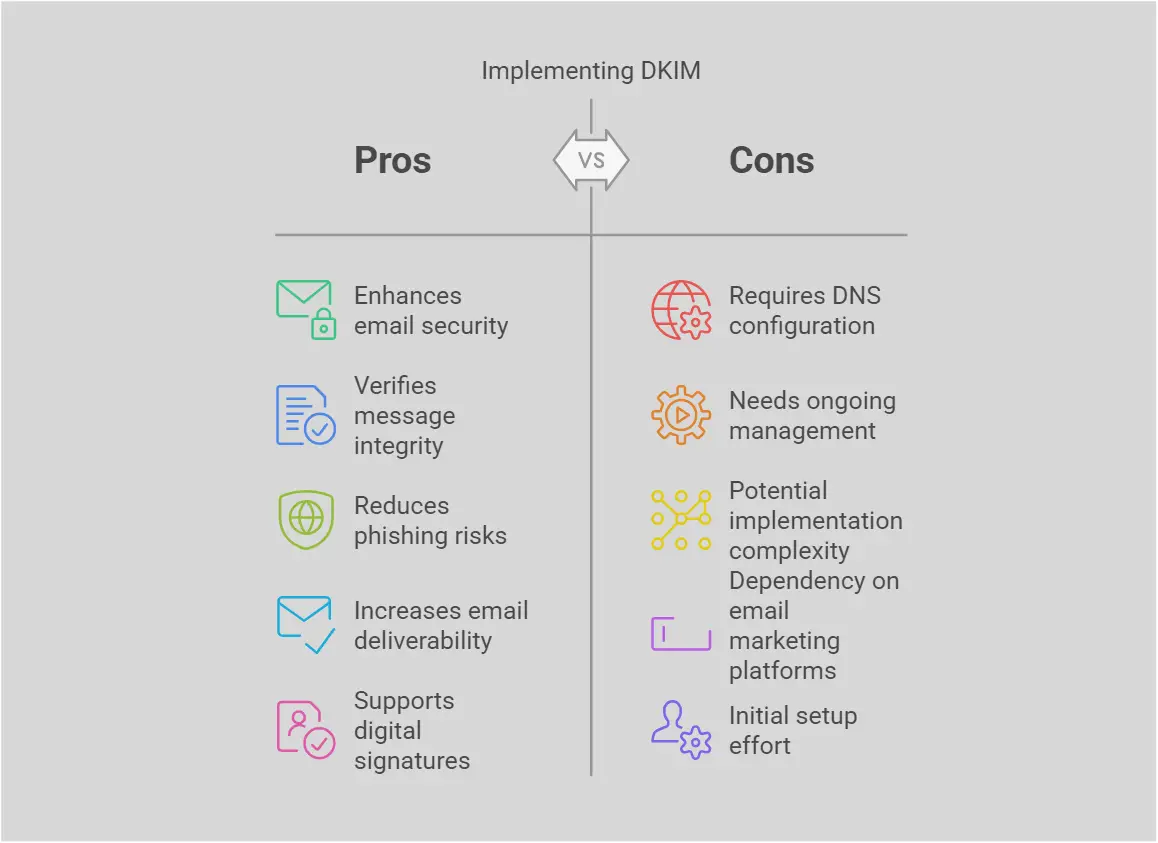
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting Conformance)
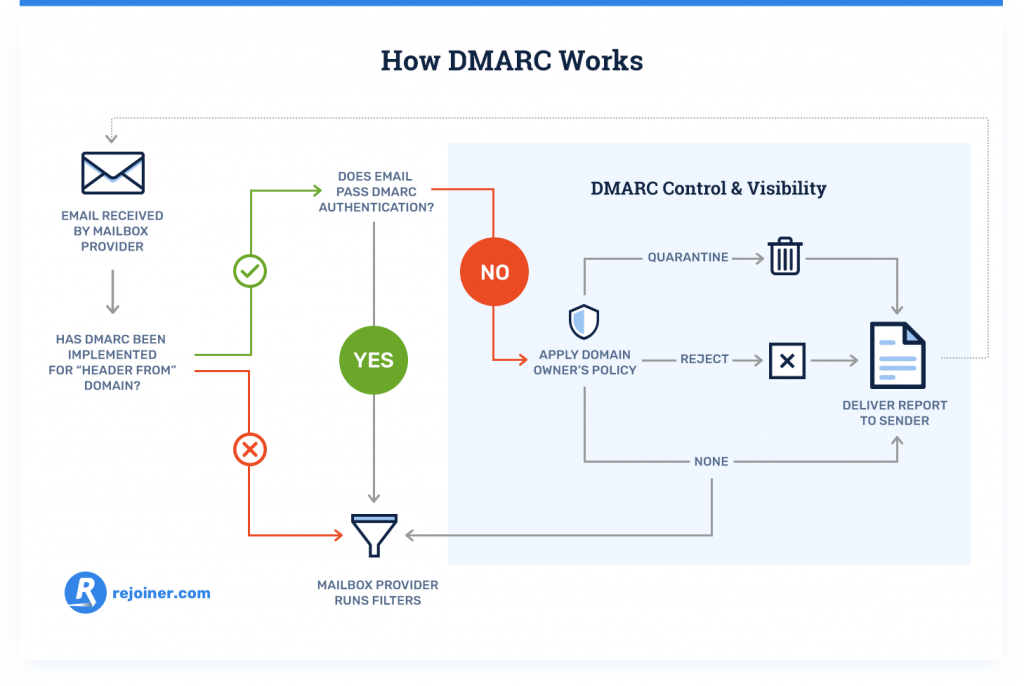
DMARC builds upon both SPF and DKIM by offering domain owners greater control over their email authentication policies. It enables organizations to publish a policy that instructs receiving servers on how to handle emails that fail SPF and/or DKIM checks.
With DMARC, domain owners can choose to quarantine or reject messages that do not pass the authentication checks, significantly reducing the chances of malicious emails reaching users’ inboxes. Additionally, DMARC provides reporting capabilities that allow organizations to monitor their email performance and identify potential abuse of their domain.
How Email Authentication Works

Understanding how email authentication works is crucial for grasping the broader implications of these protocols.
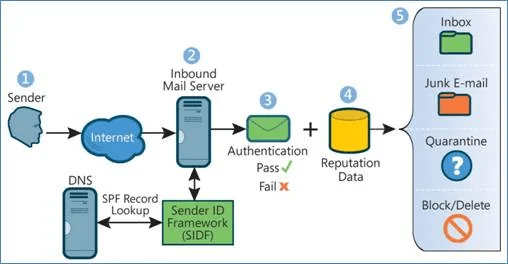
When an email is sent, the sending mail server generates specific headers containing data about the sender, the recipient, and the mail server itself. These headers play a pivotal role in the authentication process.
- Initiation of the Email Transmission Once the email is composed and sent, it travels through the internet via a series of mail servers until it reaches the recipient’s mail server.
- Verification of Authentication Protocols Upon arrival, the recipient’s mail server examines the email’s headers and utilizes SPF, DKIM, and DMARC protocols to determine the legitimacy of the message. Depending on the configurations set by the recipient’s organization, the email may be accepted, quarantined, or rejected based on the results of these checks.
- Maintenance of Security Standards Continuous monitoring and management of these authentication protocols are essential to adapt to evolving threats and maintain a strong email security posture.
The Role of Email Authentication in Cybersecurity

As phishing attacks grow more sophisticated and prevalent, the need for effective email authentication becomes increasingly pressing. By establishing robust authentication frameworks, organizations can mitigate risks and enhance their cybersecurity defenses.
Protecting Against Phishing Attacks
Phishing remains one of the most significant threats to organizations globally. Malicious actors utilize deceptive emails to trick recipients into divulging sensitive information or downloading malware.
By implementing email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, organizations create barriers against phishing attempts. These protocols help authenticate legitimate emails while identifying potentially harmful ones, minimizing the chances of successful phishing attacks.
Moreover, educating employees about recognizing phishing emails and reinforcing the importance of email authentication can further strengthen an organization’s defenses.
One of the major benefits of email authentication protocols is their ability to prevent phishing attacks. Tools like Keap and Mailchimp integrate email authentication features to ensure that email campaigns are not hijacked by malicious actors. By properly setting up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC on these platforms, businesses can protect their customers from impersonation attempts and fraudulent emails.
Enhancing Email Deliverability
Email authentication plays a crucial role in improving email deliverability rates. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) assess the credibility of incoming emails based on various factors, including the presence of authentication protocols.
Emails lacking proper authentication are more likely to be classified as spam or rejected entirely. By implementing SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, organizations can enhance their sender reputation and increase the likelihood of their emails reaching the intended recipients’ inboxes.
Reducing Spam and Fraudulent Emails
Spam and fraudulent emails contribute to a cluttered inbox, impacting productivity and hampering communication efforts. Implementing email authentication protocols allows organizations to actively filter out undesirable messages and maintain a cleaner, more efficient email environment.
Through accurate identification and verification of email sources, organizations can systematically block malicious emails, keeping their employees protected and focused on their work.
The Impact of Email Authentication on Brand Reputation
A company’s brand reputation rests on many factors, including the perceived security of its communications. Email authentication plays a pivotal role in shaping the way customers and partners view an organization.
Building Trust with Customers
In today’s digital landscape, trust is everything. Customers must feel confident that their information is secure when interacting with brands online.
By utilizing email authentication protocols, companies can demonstrate their commitment to protecting customer data and fostering safe communication channels. This proactive approach helps build stronger relationships with customers, resulting in increased loyalty and long-term business success.
Maintaining Professional Image
Organizations that take email security seriously project a more professional image. By adopting email authentication protocols, companies can minimize the risk of being impersonated or associated with fraudulent activity.
This professionalism reflects positively on the organization and can even differentiate it in a competitive market, attracting new customers who value safety and reliability.
Safeguarding Sensitive Information
Email often serves as a conduit for sensitive information, such as financial data, personal identifiers, and proprietary information. In the event of a data breach, organizations may find themselves facing devastating consequences.
Implementing email authentication protocols is a proactive measure that safeguards sensitive information from prying eyes and potential breaches. Organizations that prioritize email security ultimately protect their intellectual assets and preserve the trust of their stakeholders.
Implementing Email Authentication Protocols
To navigate the complexities of email authentication, organizations must take a strategic approach to implement these protocols effectively.
Steps to Set Up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC
Setting up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC requires a systematic approach to ensure their successful implementation. Here are some fundamental steps:
- Evaluate Current Email Infrastructure: Understand your existing email setup and determine any gaps in security. Assess the mail servers you use and identify which ones should be authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain.
- Create SPF Records: Draft an SPF record defining the allowed sending servers. Once completed, publish this record in your domain’s DNS settings.
- Generate DKIM Keys: Generate a public-private key pair for DKIM, and configure your email server to sign outgoing messages with the private key. Publish the public key in your DNS records.
- Establish DMARC Policies: Create a DMARC record that aligns with your existing SPF and DKIM setups. Include your desired policy for handling unauthorized emails and specify where you wish to receive reports regarding email delivery and authentication results.
- Monitor and Adjust: After implementation, monitor the effectiveness of the protocols. Analyze DMARC reports regularly to identify potential issues and make adjustments as needed to improve performance.
Common Challenges in Implementation
While the benefits of email authentication protocols are clear, organizations may encounter challenges during the implementation process.
- Technical Complexity: Configuring DNS records and understanding the technicalities of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC can be daunting, particularly for smaller businesses with limited IT resources. Organizations must invest time and effort into learning the nuances of each protocol to achieve effective implementation.
- Compatibility Issues: Ensuring compatibility between different email vendors and services can pose challenges. Some older systems may not fully support modern authentication methods, leading to difficulties in achieving seamless integration.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may struggle to adapt to new protocols and practices. Fostering a culture of security awareness through training can alleviate these concerns and promote a smoother transition.
Best Practices for Ongoing Management and Monitoring
Once email authentication protocols are implemented, organizations must establish best practices for ongoing management and monitoring.
- Regular Review of DNS Records: Regularly review and update DNS records to reflect changes in sending servers or email service providers. Ensuring that these records remain accurate is vital for maintaining effective email authentication.
- Conduct Periodic Audits: Perform periodic audits of your email authentication practices to identify weaknesses and areas for improvement. Consistently evaluating your email security strategy can help mitigate risks and strengthen defenses.
- Stay Informed About Emerging Threats: Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving. Stay informed about emerging trends and attack vectors to adjust your email security strategies accordingly.
Future Trends in Email Authentication

As technology continues to advance, email authentication protocols are expected to evolve in response to new threats and opportunities.
Advances in Authentication Technologies
Emerging technologies, such as blockchain and multi-factor authentication, hold promise for enhancing email security. By integrating these advancements into existing email authentication protocols, organizations can create more resilient systems capable of thwarting sophisticated attacks.
Blockchain technology, in particular, offers a decentralized approach to verify the sender’s identity, making it more challenging for attackers to spoof email addresses.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing the way organizations detect and prevent email fraud. By analyzing patterns and behaviors, AI-driven solutions can identify anomalies in email traffic, alerting administrators to potential threats before they escalate.
Additionally, automating the authentication process with AI can streamline operations, reducing the burden on IT teams while enhancing overall email security.
Regulatory Developments Impacting Email Security
As cybercrime continues to be a global concern, governments and regulatory bodies are implementing stricter guidelines governing email security. Organizations must stay abreast of these developments to ensure compliance while enhancing their email authentication practices.
For example, regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) emphasize the necessity for organizations to implement adequate security measures to protect sensitive personal data. As such, embracing email authentication protocols aligns with broader compliance efforts.
Conclusion
The significance of email authentication protocols cannot be overstated in today’s digital landscape. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the need for robust email security measures becomes increasingly crucial for organizations and individuals alike. By understanding the importance of email authentication protocols, businesses can safeguard against phishing attacks, enhance email deliverability, protect their brand reputation, and foster trust with their customers.
Through strategic implementation, continuous monitoring, and adaptation to emerging trends, organizations can create a secure and reliable email environment that promotes safe communication and bolsters their overall cybersecurity posture. Embracing email authentication protocols is not simply an option; it is a necessity in our interconnected world.